Difference between longitudinal and transverse waves Teachoo
PPT Characteristics of Light PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2664100
Light is a transverse because it will travel vertical to the medium and be right angles to it. Also light has both the electrical and magnetically components to it. So the vibrations of the particles in the light waves have the ability to travel even in the vacuum.

Transverse vs Longitudinal Waves Difference and Comparison
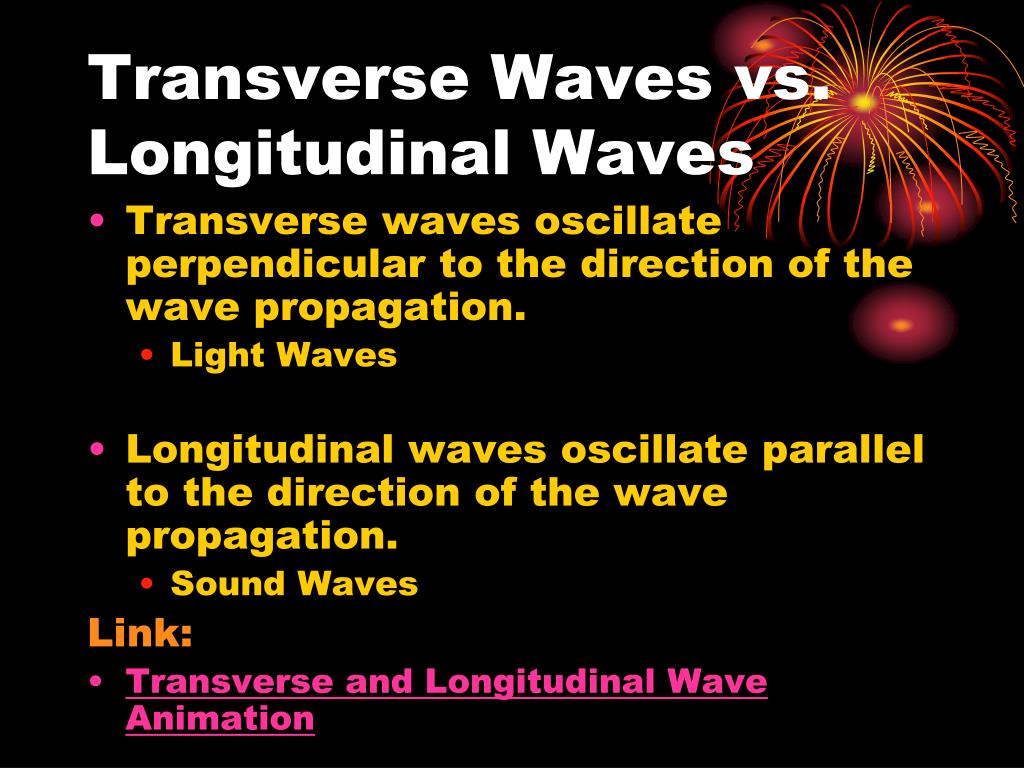
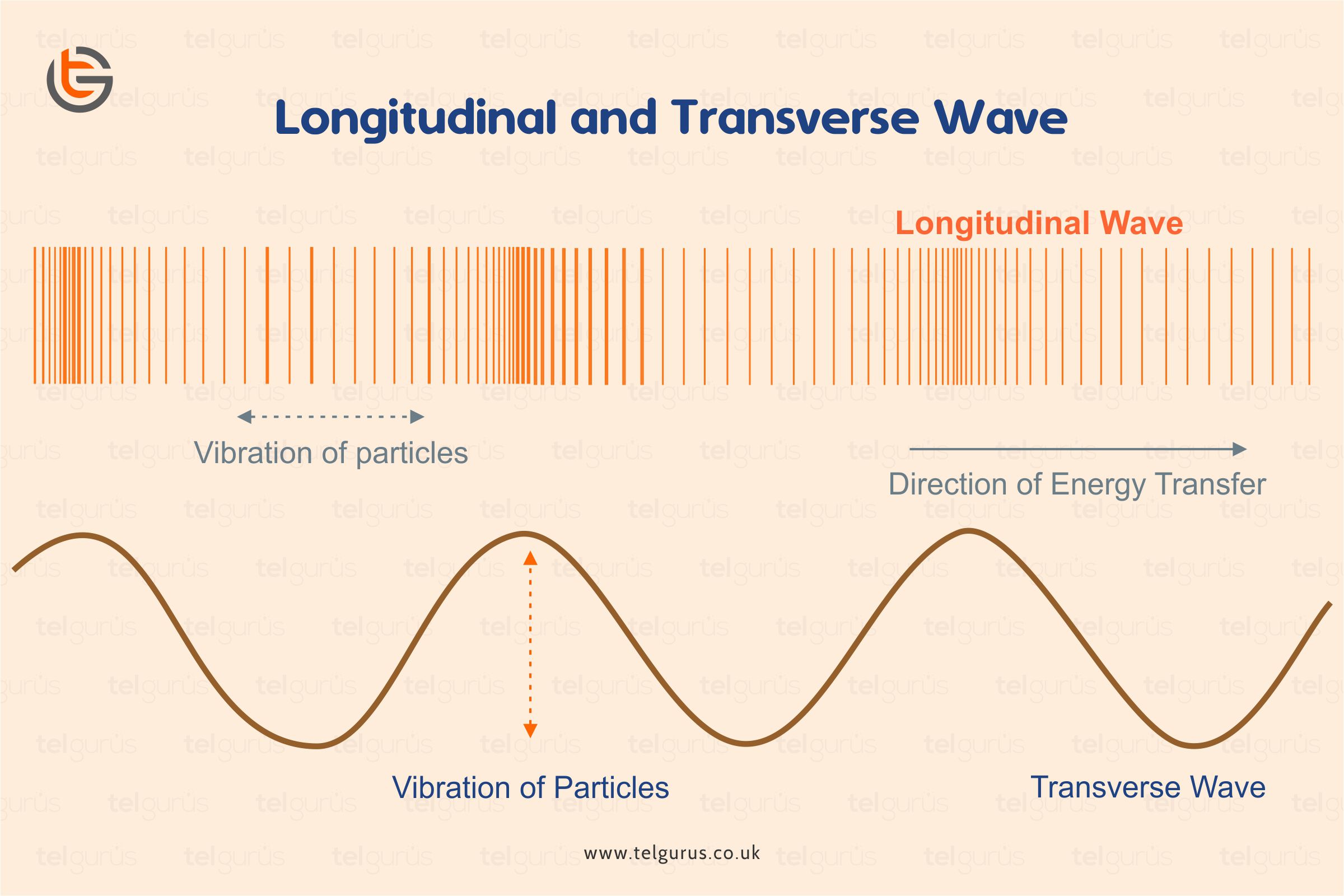
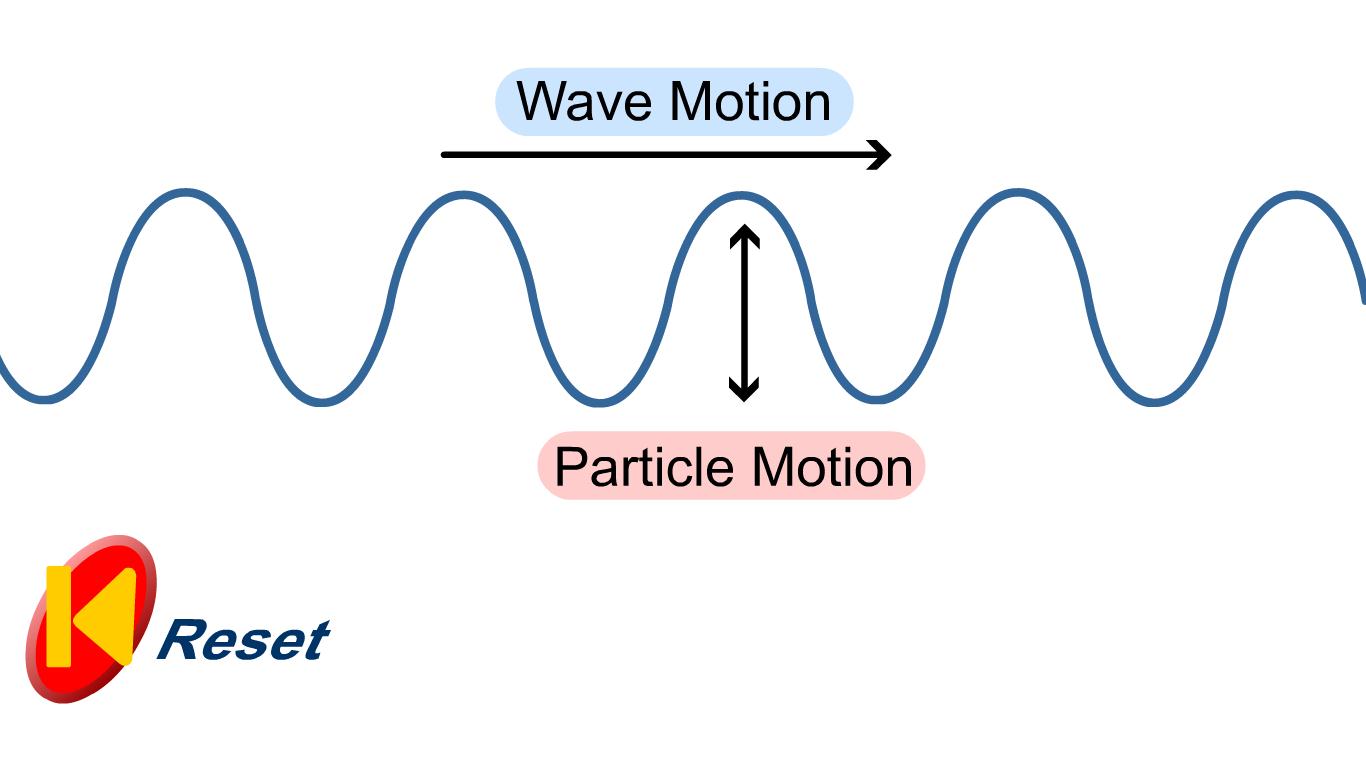
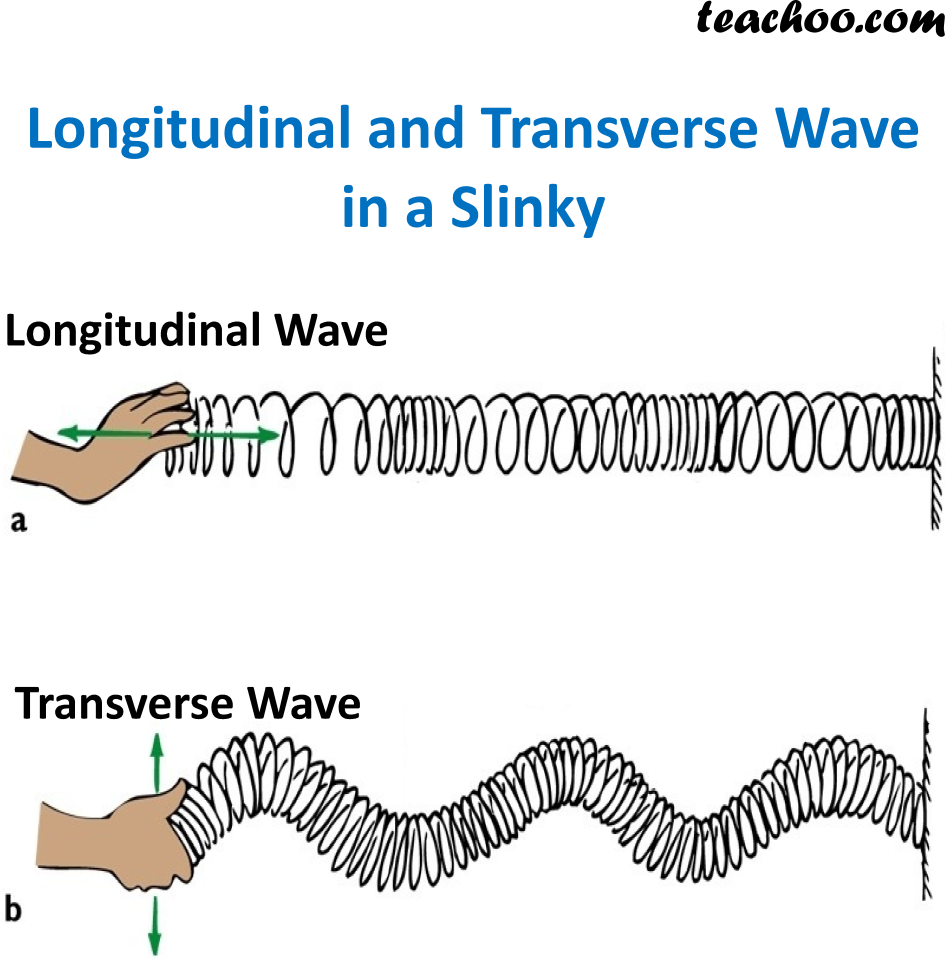
In physics, a transverse wave is a wave that oscillates perpendicularly to the direction of the wave's advance. In contrast, a longitudinal wave travels in the direction of its oscillations. All waves move energy from place to place without transporting the matter in the transmission medium if there is one.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Water waves: Water waves are an example of both longitudinal and transverse waves. The movement of particles in water waves is in a clockwise direction. While the movement of the waves is in a transverse manner. We also need to understand that the radius of the particles decreases with an increase in the depth of the water.

6 Illustration of a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave Download Scientific Diagram
Light waves are purely transverse, while sound waves are purely longitudinal. Ocean waves are a peculiar mixture of transverse and longitudinal, with parcels of water moving in elliptical trajectories as waves pass. Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation. The undulations in an electromagnetic wave occur in the electric and magnetic fields.

Properties of waves and wave cycles. Scalar, transverse, energy and more. Chris Plouffe
A wave is a disturbance that travels or propagates from the place where it was created. Waves transfer energy from one place to another, but they do not necessarily transfer any mass. Light, sound, and waves in the ocean are common examples of waves. Sound and water waves are mechanical waves; meaning, they require a medium to travel through.

Transverse And Longitudinal Waves Wavelength And Propagation Speed Periodic Motion MCAT Content
Properties of waves - Edexcel Longitudinal and transverse waves. Waves are one way in which energy may be transferred between stores. Both mechanical and electromagnetic waves will transfer energy.

Explainer making waves in science
In contrast, in longitudinal waves, such as sound waves in a liquid or gas, the displacement of the particles in the oscillation is always in the direction of propagation, so these waves do not exhibit polarization. Transverse waves that exhibit polarization include electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves, gravitational waves,[6.
Frazer does Physics 3.2 Longitudinal and Transverse Waves
Conclusion. Light waves are an example of transverse waves, because the waves move at a 90-degree angle to the direction in which the energy is traveling. Light waves do not need a medium to transfer energy through—they can travel through vacuums, which is how we get light from the sun and the far-away stars in our universe.

Anatomy of a Transverse Wave? YouTube
Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that can be detected by the eye. It travels as a transverse wave. Unlike a sound waves, light waves do not need a medium to pass through, they can.
Longitudinal and Transverse Waves Explanation, Difference Teachoo
Many assume that transverse waves only occur on the surface of mediums, like the surface of water, while longitudinal waves are restricted to the interior of materials. Transverse waves can also propagate within a medium, just like light through a glass prism. Similarly, while sound (a longitudinal wave) often travels within a medium like air.

Transverse Wave and Longitudinal Wave Jennifer Hemmings
All the electromagnetic waves - eg light waves, microwaves, radio waves, x-rays. S type earthquake waves. One way of remembering that an S type earthquake wave is a transverse is that an S looks.

Difference between longitudinal and transverse waves Teachoo
There are two types of waves: Longitudinal; Transverse;. Examples of transverse waves include light, water, and Mexican waves! Transverse waves have peaks/crests and troughs. The amplitude of the wave is the distance from the central point to a peak or a trough (the maximum displacement of the wave). The wavelength of the wave (given the.
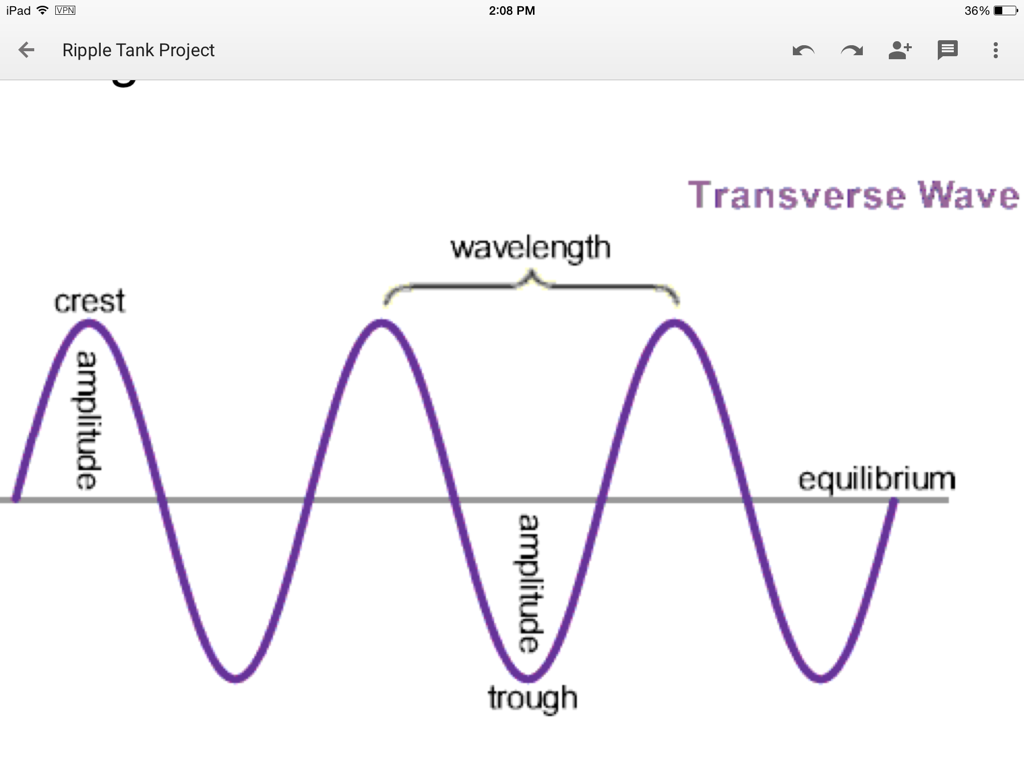
Waves Part 1
Longitudinal and transverse waves can combine to form what is known as a surface wave. One common example of this combination is the Rayleigh wave. In a Rayleigh wave, particles move in an elliptical or circular motion, combining both the back-and-forth (transverse) and compressional (longitudinal) motions.

Are Light Waves Transverse or Longitudinal? The Interesting Answer! Optics Mag
The diagrams of diffraction you have shared don't show light as a longitudinal wave, they are a completely different representation of waves. The lines represent wave fronts NOT compression & rarefaction. Wave fronts can be thought of as corresponding to wave crests, but really mean points on waves that are in phase with one another.

Transverse vs Longitudinal Wave Leverage Edu
Metrics. Electromagnetic fields in light waves are mainly transverse to propagation direction but actually also have longitudinal components, which may give rise to unexpected optical phenomena.
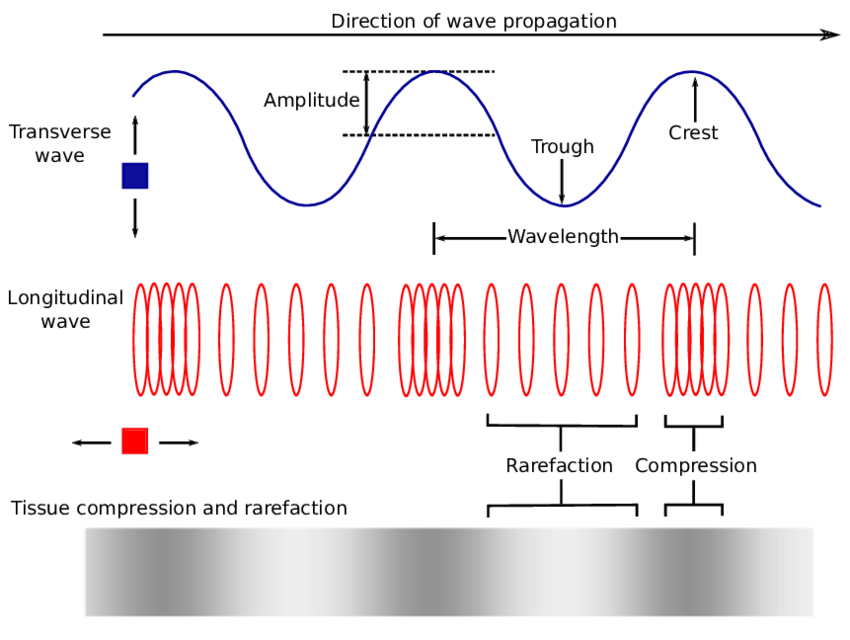
Wave, its types and characteristics Online Science Notes
This unit is concerned with describing the properties of harmonic oscillations and wave motion. The first half of the unit covers such topics as resonance, transients, coupled oscillators, transverse and longitudinal waves. The second half looks at interference and diffraction, firstly as important properties of waves in general, and then using.